|
11.03.2014
Efficient Project Management with it Toolset
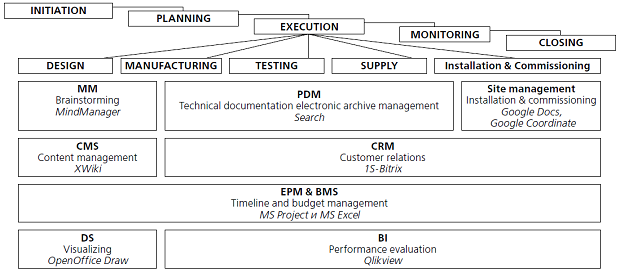
“Managers, like pilots, need instrumentation about many aspects of their environment and performance to monitor the journey toward excellent future outcomes” [Kaplan and Norton] The processes of systematization, arrangement and management of the sophisticated information flow that arises during implementation of the complex projects can be organized through development and application of individual (specially created for the project) or standard (borrowed) tools based on the software solutions. The main software platforms include MS Office products, Business Intelligence systems, remote collaborative software (groupware), and integrated cloud services for project the management. With three classical constraints of the project management (time, cost, scope) the effective results can be achieved if the tools (including hardware and software solutions) interaction is provided at the system level. One of the similar system solutions for the information flow management in a major project was developed by the authors of this article together with the project team during a number of the oil & gas integrated projects implementation in 2009-2013. The earlier published paper presents eight characteristics of the project management tools. The key ones are simplicity, clarity, visualization, simultaneous remote sharing & use, tools versatility (see Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Information management tools system in a major project. As integrating element of the project management system the “Search” software solution of the Product Data Management (PDM) software regulates management of the project docflow and electronic archive of the project scope technical documentation. These operations are implemented in the PDMsystem with differential access rights, backup function and unauthorized access protection. As an example, the system provides possibility within a few minutes to find and apply necessary technical documents from the tens of thousands ones regarding all types of equipment applicable in ongoing projects. The mind mapping technique is widely used in development of the project’s Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). The ideas generated in brainstorming are combined into a summary mind map using Mind- Manager, FreeMind, XMind, ConceptDraw MindMap and other software for subsequent analysis and generation of the new ideas. The mentioned software implements composition of the checklists for individual processes (Fig. 2), short-term planning with implementation control, visualization and arrangement of large amounts of information for a rapid analysis and decision making. Some software solutions apply the customized templates libraries of the project management tools. For example, the Jetpack expansion for MindManager brings project charter, status report, risk management plan and other tools (see Fig. 2).
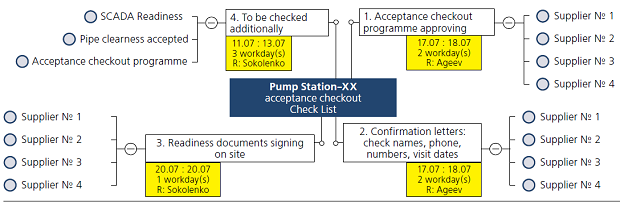
Figure 2. A checklist of the oil pumping station’s status for an acceptance checkout in the Purpe-Samotlor project implemented by HMS Group in 2011. Microsoft Project, Primavera, Spider Project, GanttProject, Turbo Project and other software is the most widely used at present for the time constraints management in projects. The light client-server solutions and web services are commonly applied as well. Microsoft Project is employed in the major projects to create a comprehensive network chart, bottlenecks diagrams, plan/ fact analysis, and the results are applied to correct the project management course. The planning and reporting on the project implementation can be done together with customers and subcontractors with automated weekly reports at that. Google Docs, ZOHO Docs can be used for remote control of installation and commissioning works at the project construction site. Objectives for the representative offices at the weekly meetings are set in the forms developed in the Google Docs tables. The regional managers receive all the necessary information about the task from their PDAs and transmit their reports on the works status.
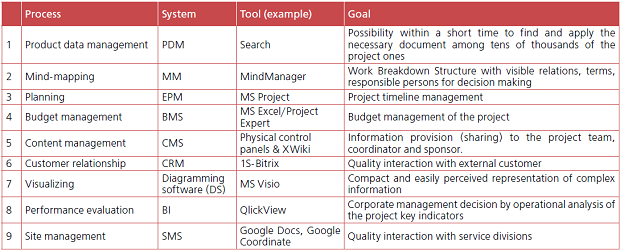
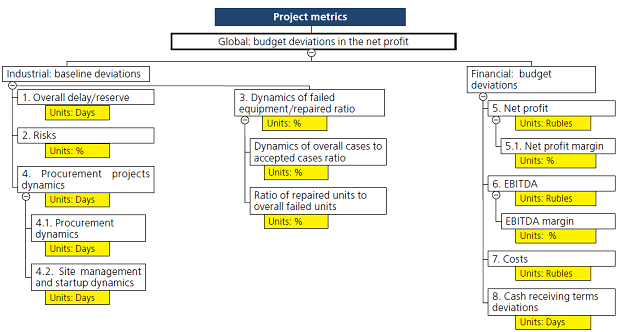
Table 1: Processes, tools and goals of information management in major projects. At the project’s phases “Execution” and “Monitoring” it is particularly important for the project team to ensure decision-making efficiency at potential deviation off the planned indicators. Alike the pilot’s dashboard, the project control center tools currently implement metrics and the key performance indicators combined into the control panels. The Business Intelligence class software providing the opportunity to work with those tools is presented by such solutions as QlickView, IBM Cognos, SAP BusinessObjects, Contour BI and several dozen other systems. In relevant software a base model of the measurable indicators (metrics) is chosen as necessary and sufficient for the project effectiveness evaluation and feasible for the project course control. For major projects it is recommended to apply eight key metrics (Fig. 3). Being implemented in the control panel interface in a tablet of CEO or the project office leader, the metrics change information helps to make effective decisions at the company’s projects portfolio management (see Fig. 3).
Fig. 3. Major project metrics model. As a necessary result of operation, the project information management tools system shall find its reflection in the company’s specific “body of knowledge” as a meta-tool - a library of tools to support the company’s operations management processes. A library of the best practices and lessons learned from own and borrowed experience is formed for subsequent share use at that. The projects team shall actively support this corporate database of cases, including internal competencies exchange programs. CONCLUSION/FINDINGS
HMS Group
References
 Download
(400.5KB) Download
(400.5KB)
|
USEFUL LINKS
|
- ProjectsSupporting materials
- | About us
- | Products
- | Services
- | Press-centre
- | Projects
- | Supporting materials
- | Contacts
- | Site map
125252, Moscow, 12 Aviakonstructor Mikoyan street
Phone: +7 (495) 664-81-71, fax: +7 (495) 664-81-72