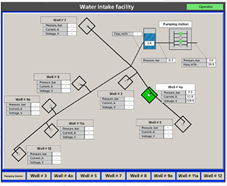
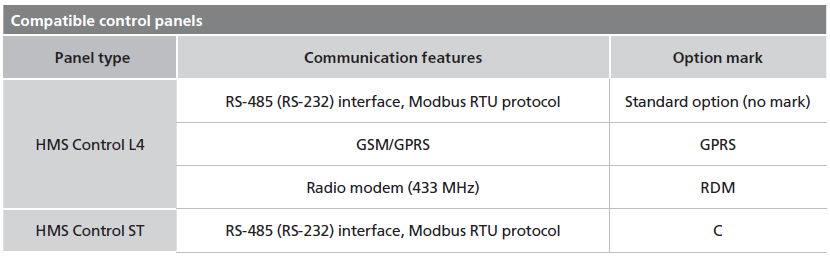
|
USEFUL LINKS
Сontacts: |
- ProjectsSupporting materials
- | About us
- | Products
- | Services
- | Press-centre
- | Projects
- | Supporting materials
- | Contacts
- | Site map
125252, Moscow, 12 Aviakonstructor Mikoyan street
Phone: +7 (495) 664-81-71, fax: +7 (495) 664-81-72